20 Multiple Regression with many predictors
20.1 R setup for this chapter
Appendix A lists all R packages used in this book, and also provides R session information.
Multiple regression y predicted by 3-15 variables
20.2 Data is bodyfat
Appendix C provides further guidance on pulling data from other systems into R, while Appendix D gives more information (including download links) for all data sets used in this book.
My source for these data was Kaggle, although the data have been published in several other places. The data describe 252 men whose percentage of body fat was determined via underwater weighing and Siri’s (1956) equation.
From Kaggle:
These data are used to produce the predictive equations for lean body weight given in the abstract “Generalized body composition prediction equation for men using simple measurement techniques”, K.W. Penrose, A.G. Nelson, A.G. Fisher, FACSM, Human Performance Research Center, Brigham Young University, Provo, Utah 84602 as listed in Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise, vol. 17, no. 2, April 1985, p. 189.
bodyfat <- read_csv("data/bodyfat.csv", show_col_types = FALSE) |>
janitor::clean_names()
bodyfat# A tibble: 248 × 16
kag_row density siri_bf age weight height neck chest abdomen hip thigh
<chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 sub_001 1.07 12.3 23 154. 67.8 36.2 93.1 85.2 94.5 59
2 sub_002 1.09 6.1 22 173. 72.2 38.5 93.6 83 98.7 58.7
3 sub_003 1.04 25.3 22 154 66.2 34 95.8 87.9 99.2 59.6
4 sub_004 1.08 10.4 26 185. 72.2 37.4 102. 86.4 101. 60.1
5 sub_005 1.03 28.7 24 184. 71.2 34.4 97.3 100 102. 63.2
6 sub_006 1.05 21.3 24 210. 74.8 39 104. 94.4 108. 66
7 sub_007 1.05 19.2 26 181 69.8 36.4 105. 90.7 100. 58.4
8 sub_008 1.07 12.4 25 176 72.5 37.8 99.6 88.5 97.1 60
9 sub_009 1.09 4.1 25 191 74 38.1 101. 82.5 99.9 62.9
10 sub_010 1.07 11.7 23 198. 73.5 42.1 99.6 88.6 104. 63.1
# ℹ 238 more rows
# ℹ 5 more variables: knee <dbl>, ankle <dbl>, biceps <dbl>, forearm <dbl>,
# wrist <dbl>The variables included are:
| Variable | Description1 |
|---|---|
kag_row |
subject identification code |
density |
density determined from underwater weighing |
siri_bf |
percent body fat from Siri’s (1956) equation2 |
age |
age (years) |
weight |
weight (pounds) |
height |
height (inches) |
neck |
neck circumference (cm) |
chest |
chest circumference (cm) |
abdomen |
abdomen circumference (cm) |
hip |
hip circumference (cm) |
thigh |
thigh circumference (cm) |
knee |
knee circumference (cm) |
ankle |
ankle circumference (cm) |
biceps |
biceps (extended) circumference (cm) |
forearm |
forearm circumference (cm) |
wrist |
wrist circumference (cm) |
As Kaggle motivates,
Accurate measurement of body fat is inconvenient/costly and it is desirable to have easy methods of estimating body fat that are not inconvenient/costly.
So our job will be to predict the siri_bf measure using the 13 predictors listed above from age through wrist, or perhaps a well-chosen subset of those predictors.
Note that we have no missing data here to worry about.
n_miss(bodyfat)[1] 0Since our main goal is making accurate predictions, it’s appealing to validate our models in new data. We might split into training and testing samples
20.3 Need for transformation?
We’ll start by considering whether the Box-Cox approach suggests any particular transformation for our outcome variable when we fit a kitchen sink model (e.g., a model including main effects of all available predictors.)
fit1 <- lm(
siri_bf ~ age + weight + height + neck + chest +
abdomen + hip + thigh + knee + ankle + biceps +
forearm + wrist,
data = bodyfat
)
boxCox(fit1)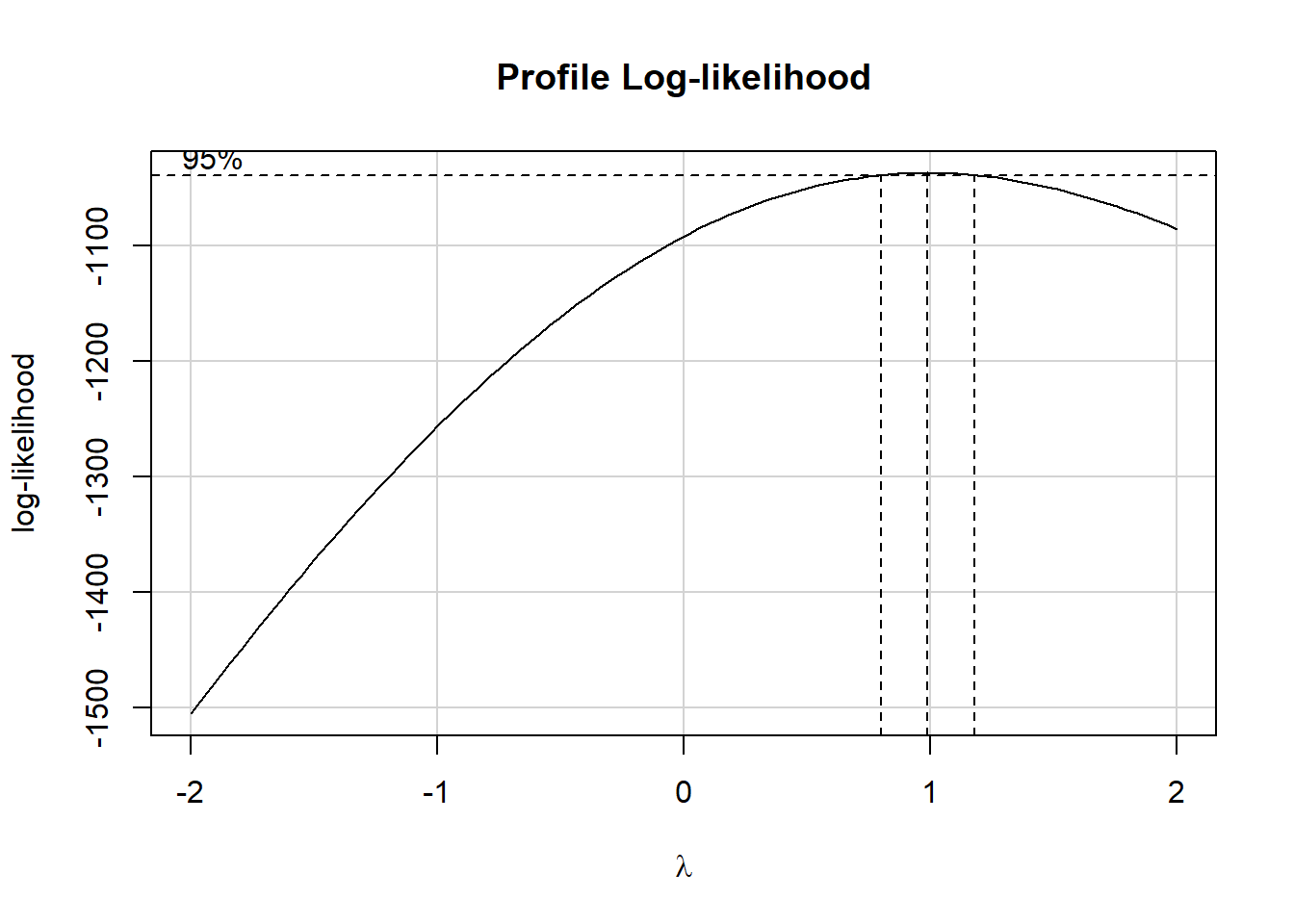
Since the recommended power transformation parameter \(\lambda\) is quite close to 1, we’ll not be using any transformation in this chapter.
20.4 The Full OLS model
model_parameters(fit1, ci = 0.95)Parameter | Coefficient | SE | 95% CI | t(234) | p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
(Intercept) | -14.73 | 22.35 | [-58.77, 29.30] | -0.66 | 0.510
age | 0.05 | 0.03 | [ -0.01, 0.11] | 1.53 | 0.128
weight | -0.09 | 0.06 | [ -0.21, 0.04] | -1.40 | 0.162
height | -0.08 | 0.18 | [ -0.44, 0.27] | -0.46 | 0.644
neck | -0.48 | 0.23 | [ -0.94, -0.02] | -2.06 | 0.040
chest | -0.03 | 0.10 | [ -0.23, 0.18] | -0.27 | 0.786
abdomen | 0.97 | 0.09 | [ 0.79, 1.14] | 10.69 | < .001
hip | -0.21 | 0.15 | [ -0.50, 0.08] | -1.45 | 0.148
thigh | 0.20 | 0.15 | [ -0.09, 0.49] | 1.36 | 0.176
knee | 0.04 | 0.25 | [ -0.45, 0.52] | 0.14 | 0.886
ankle | 0.17 | 0.22 | [ -0.27, 0.61] | 0.78 | 0.436
biceps | 0.16 | 0.17 | [ -0.18, 0.50] | 0.93 | 0.354
forearm | 0.44 | 0.20 | [ 0.05, 0.83] | 2.21 | 0.028
wrist | -1.59 | 0.53 | [ -2.64, -0.54] | -2.98 | 0.003
Uncertainty intervals (equal-tailed) and p-values (two-tailed) computed
using a Wald t-distribution approximation.check_model(fit1)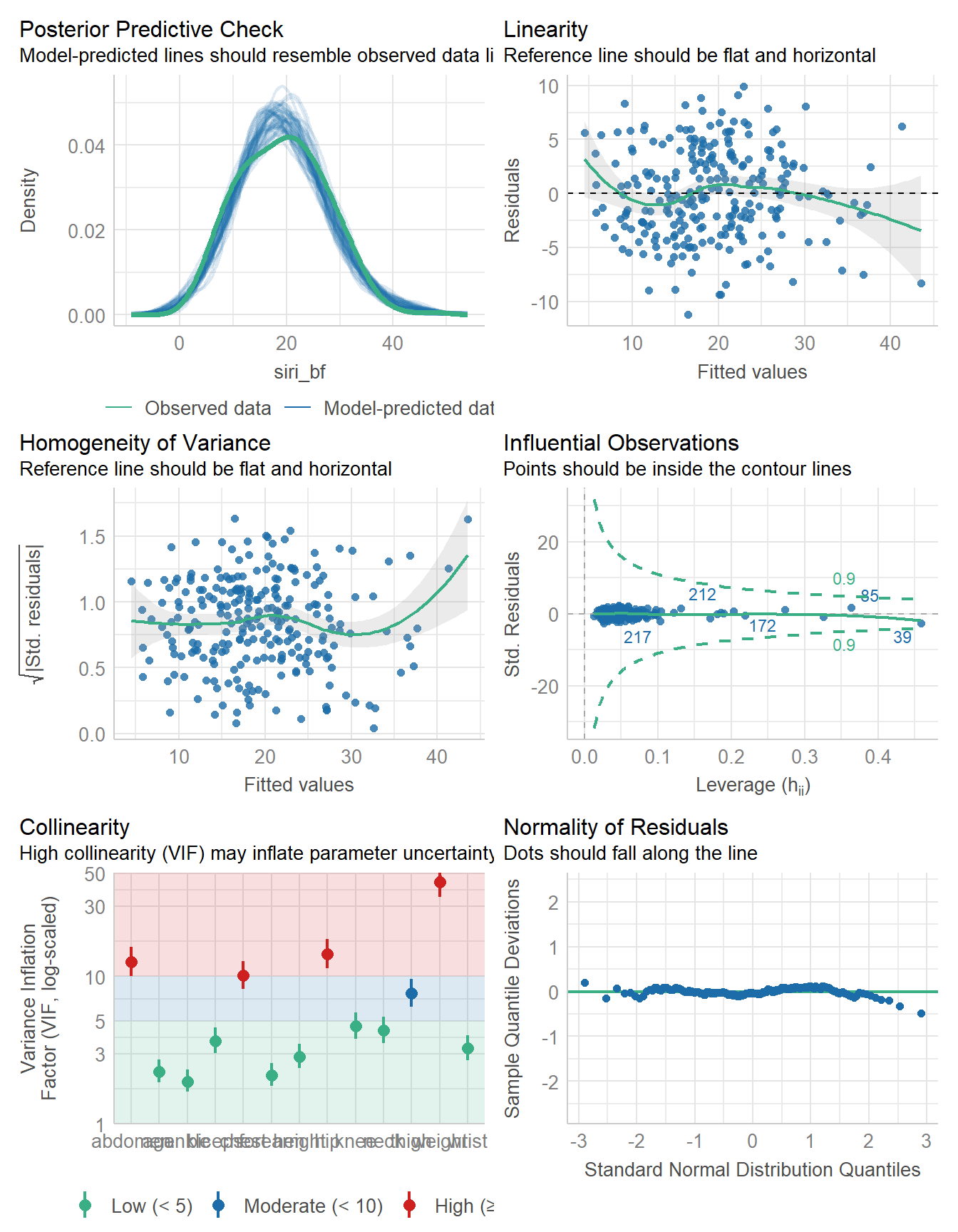
model_performance(fit1)# Indices of model performance
AIC | AICc | BIC | R2 | R2 (adj.) | RMSE | Sigma
------------------------------------------------------------------
1440.004 | 1442.073 | 1492.706 | 0.742 | 0.728 | 4.153 | 4.27520.5 Identify a predictor subset with backwards stepwise elimination
fit2 <- select_parameters(fit1)
model_parameters(fit2, ci = 0.95)Parameter | Coefficient | SE | 95% CI | t(239) | p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
(Intercept) | -19.90 | 11.68 | [-42.91, 3.11] | -1.70 | 0.090
age | 0.05 | 0.03 | [ -0.01, 0.11] | 1.67 | 0.096
weight | -0.09 | 0.04 | [ -0.17, -0.01] | -2.21 | 0.028
neck | -0.47 | 0.22 | [ -0.91, -0.03] | -2.12 | 0.035
abdomen | 0.96 | 0.07 | [ 0.82, 1.10] | 13.32 | < .001
hip | -0.21 | 0.14 | [ -0.48, 0.07] | -1.49 | 0.136
thigh | 0.26 | 0.13 | [ 0.00, 0.51] | 1.99 | 0.048
forearm | 0.49 | 0.19 | [ 0.13, 0.86] | 2.65 | 0.008
wrist | -1.46 | 0.51 | [ -2.47, -0.46] | -2.88 | 0.004
Uncertainty intervals (equal-tailed) and p-values (two-tailed) computed
using a Wald t-distribution approximation.compare_models(fit1, fit2)Parameter | fit1 | fit2
--------------------------------------------------------------
(Intercept) | -14.73 (-58.77, 29.30) | -19.90 (-42.91, 3.11)
age | 0.05 ( -0.01, 0.11) | 0.05 ( -0.01, 0.11)
weight | -0.09 ( -0.21, 0.04) | -0.09 ( -0.17, -0.01)
neck | -0.48 ( -0.94, -0.02) | -0.47 ( -0.91, -0.03)
abdomen | 0.97 ( 0.79, 1.14) | 0.96 ( 0.82, 1.10)
hip | -0.21 ( -0.50, 0.08) | -0.21 ( -0.48, 0.07)
thigh | 0.20 ( -0.09, 0.49) | 0.26 ( 0.00, 0.51)
forearm | 0.44 ( 0.05, 0.83) | 0.49 ( 0.13, 0.86)
wrist | -1.59 ( -2.64, -0.54) | -1.46 ( -2.47, -0.46)
chest | -0.03 ( -0.23, 0.18) |
ankle | 0.17 ( -0.27, 0.61) |
height | -0.08 ( -0.44, 0.27) |
knee | 0.04 ( -0.45, 0.52) |
biceps | 0.16 ( -0.18, 0.50) |
--------------------------------------------------------------
Observations | 248 | 248Note that fit2 drops five of the 13 predictors from the fit1 model.
check_model(fit2)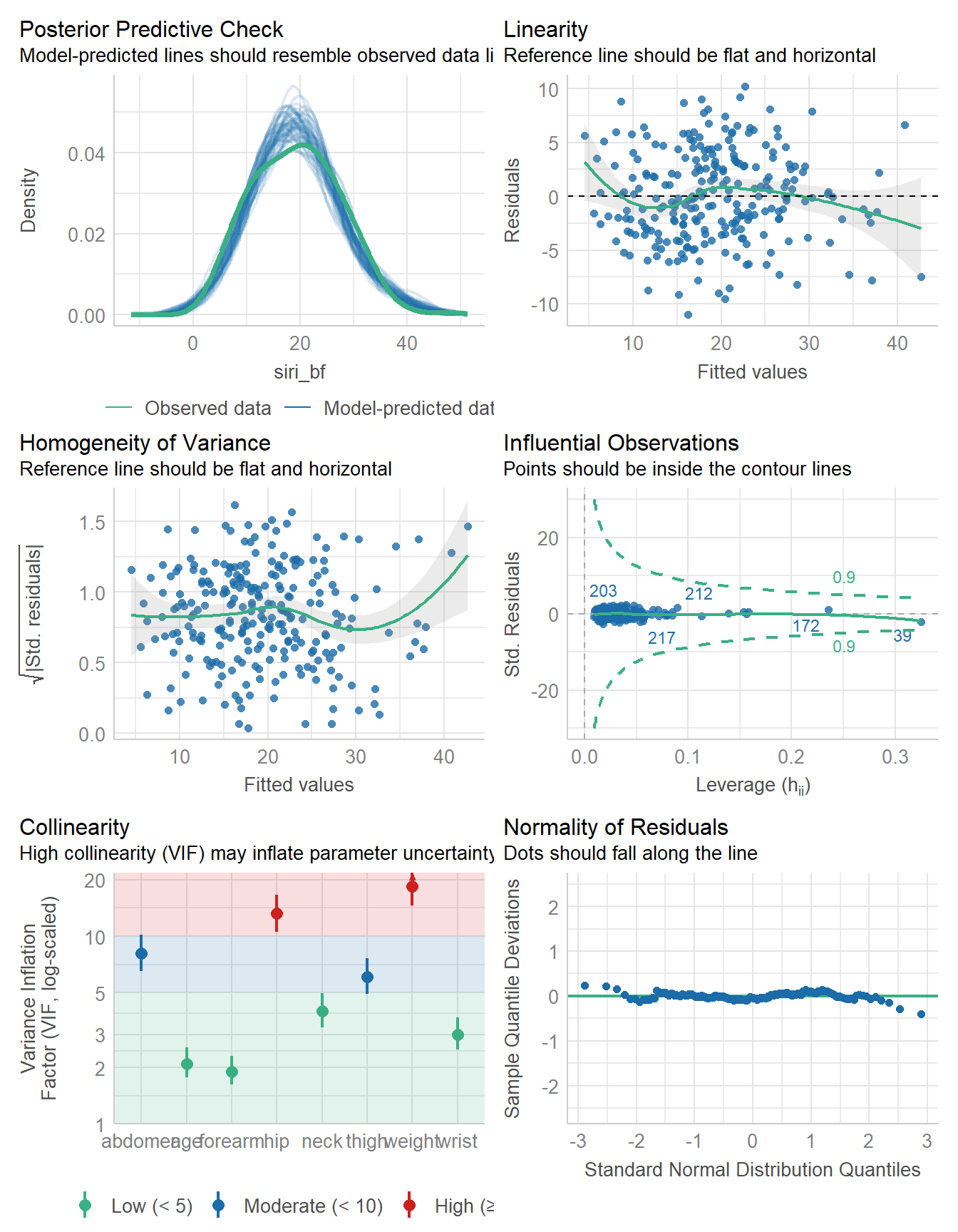
model_performance(fit2)# Indices of model performance
AIC | AICc | BIC | R2 | R2 (adj.) | RMSE | Sigma
------------------------------------------------------------------
1431.933 | 1432.861 | 1467.067 | 0.740 | 0.732 | 4.169 | 4.247compare_performance(fit1, fit2)# Comparison of Model Performance Indices
Name | Model | AIC (weights) | AICc (weights) | BIC (weights) | R2 | R2 (adj.) | RMSE | Sigma
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
fit1 | lm | 1440.0 (0.017) | 1442.1 (0.010) | 1492.7 (<.001) | 0.742 | 0.728 | 4.153 | 4.275
fit2 | lm | 1431.9 (0.983) | 1432.9 (0.990) | 1467.1 (>.999) | 0.740 | 0.732 | 4.169 | 4.247plot(compare_performance(fit1, fit2))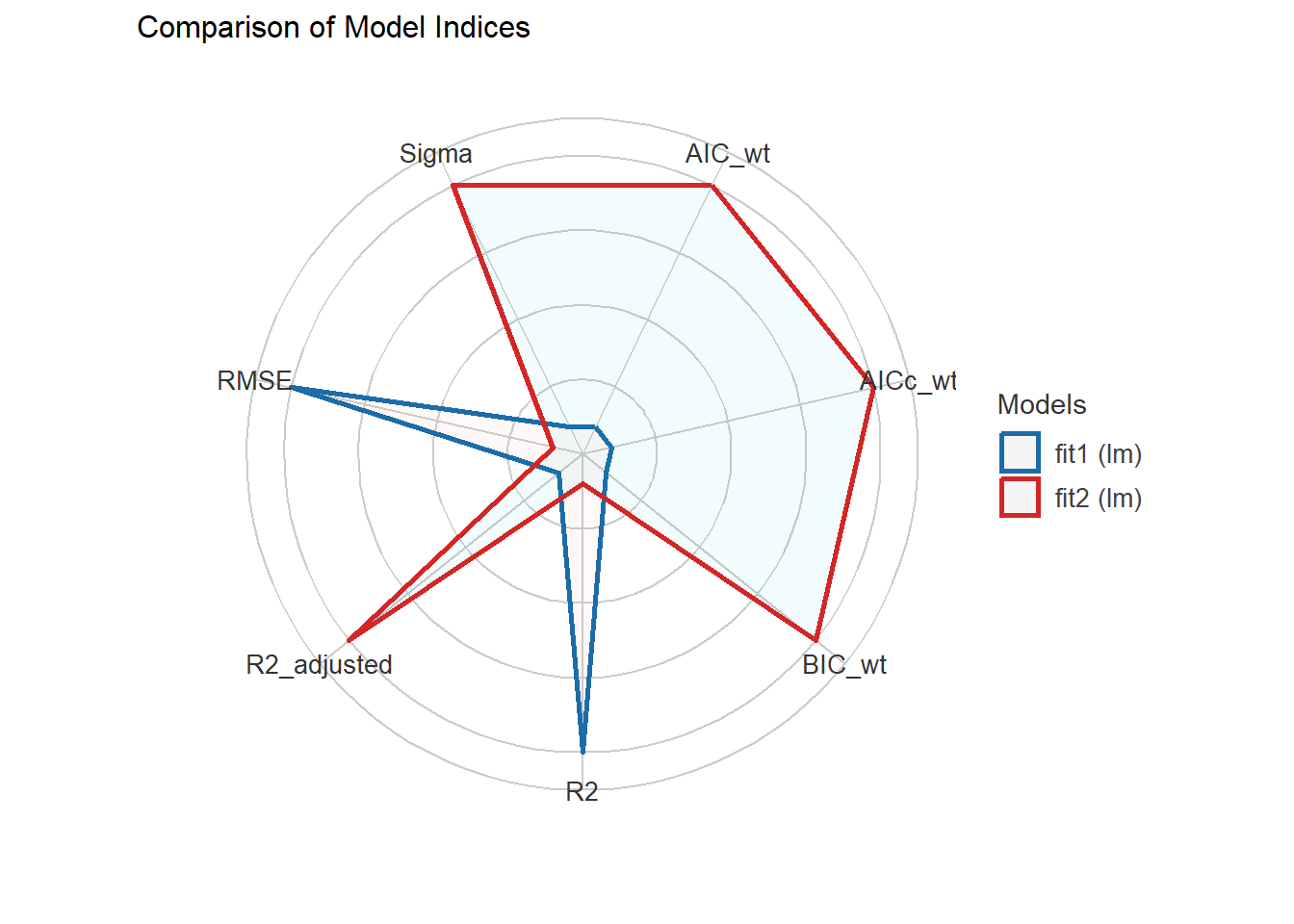
performance_mae(fit1)[1] 3.418899performance_mae(fit2)[1] 3.412077performance_rmse(fit1)[1] 4.15292performance_rmse(fit2)[1] 4.169102set.seed(431)
performance_accuracy(fit1, method = "cv", k = 5)# Accuracy of Model Predictions
Accuracy (95% CI): 81.49% [73.12%, 92.09%]
Method: Correlation between observed and predictedset.seed(431)
performance_accuracy(fit2, method = "cv", k = 5)# Accuracy of Model Predictions
Accuracy (95% CI): 82.87% [74.24%, 93.11%]
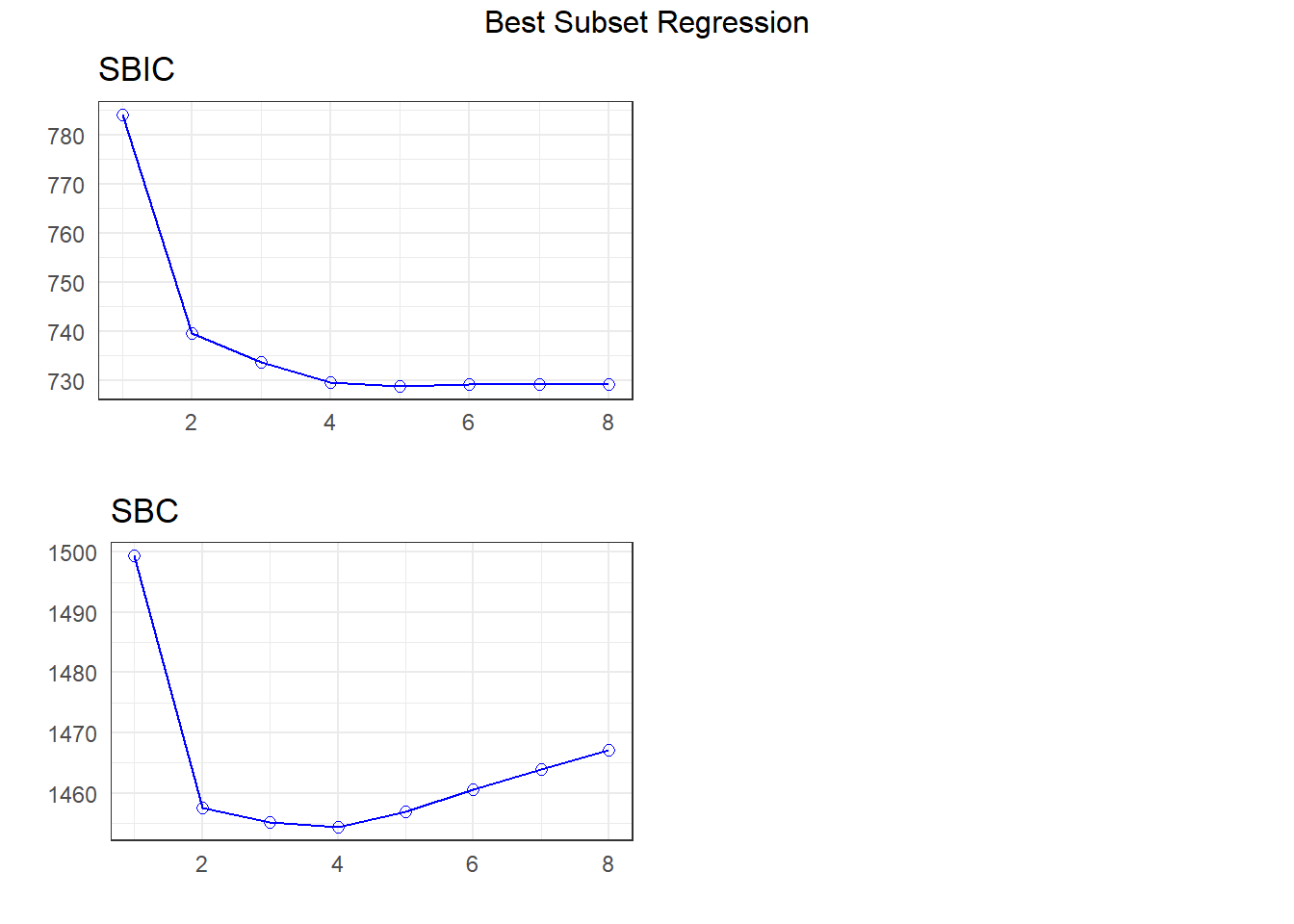
Method: Correlation between observed and predicted20.6 Best Subsets Regression and Mallows’ \(C_p\)
k <- ols_step_best_subset(fit1,
max_order = 8,
metric = "cp")k Best Subsets Regression
--------------------------------------------------------------
Model Index Predictors
--------------------------------------------------------------
1 abdomen
2 weight abdomen
3 weight abdomen wrist
4 weight abdomen forearm wrist
5 weight neck abdomen forearm wrist
6 weight neck abdomen biceps forearm wrist
7 age weight neck abdomen thigh forearm wrist
8 age weight neck abdomen hip thigh forearm wrist
--------------------------------------------------------------
Subsets Regression Summary
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Adj. Pred
Model R-Square R-Square R-Square C(p) AIC SBIC SBC MSEP FPE HSP APC
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 0.6543 0.6529 0.6438 69.8409 1488.8082 784.0875 1499.3485 5783.2127 23.5075 0.0952 0.3513
2 0.7143 0.7120 0.7047 17.3601 1443.5224 739.4622 1457.5761 4798.8699 19.5840 0.0793 0.2927
3 0.7233 0.7199 0.7104 11.1761 1437.5707 733.6757 1455.1379 4666.5692 19.1197 0.0774 0.2857
4 0.7304 0.7259 0.7159 6.8132 1433.2074 729.5437 1454.2879 4567.1491 18.7863 0.0761 0.2807
5 0.7335 0.7280 0.7175 5.9241 1432.2633 728.7699 1456.8573 4531.9786 18.7150 0.0758 0.2797
6 0.7355 0.7290 0.7176 6.1051 1432.3916 729.0562 1460.4990 4516.6449 18.7247 0.0759 0.2798
7 0.7378 0.7302 0.7175 6.0319 1432.2408 729.1139 1463.8617 4496.3797 18.7135 0.0759 0.2797
8 0.7403 0.7316 0.7186 5.8272 1431.9331 729.0634 1467.0674 4473.4501 18.6905 0.0758 0.2793
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
AIC: Akaike Information Criteria
SBIC: Sawa's Bayesian Information Criteria
SBC: Schwarz Bayesian Criteria
MSEP: Estimated error of prediction, assuming multivariate normality
FPE: Final Prediction Error
HSP: Hocking's Sp
APC: Amemiya Prediction Criteria plot(k)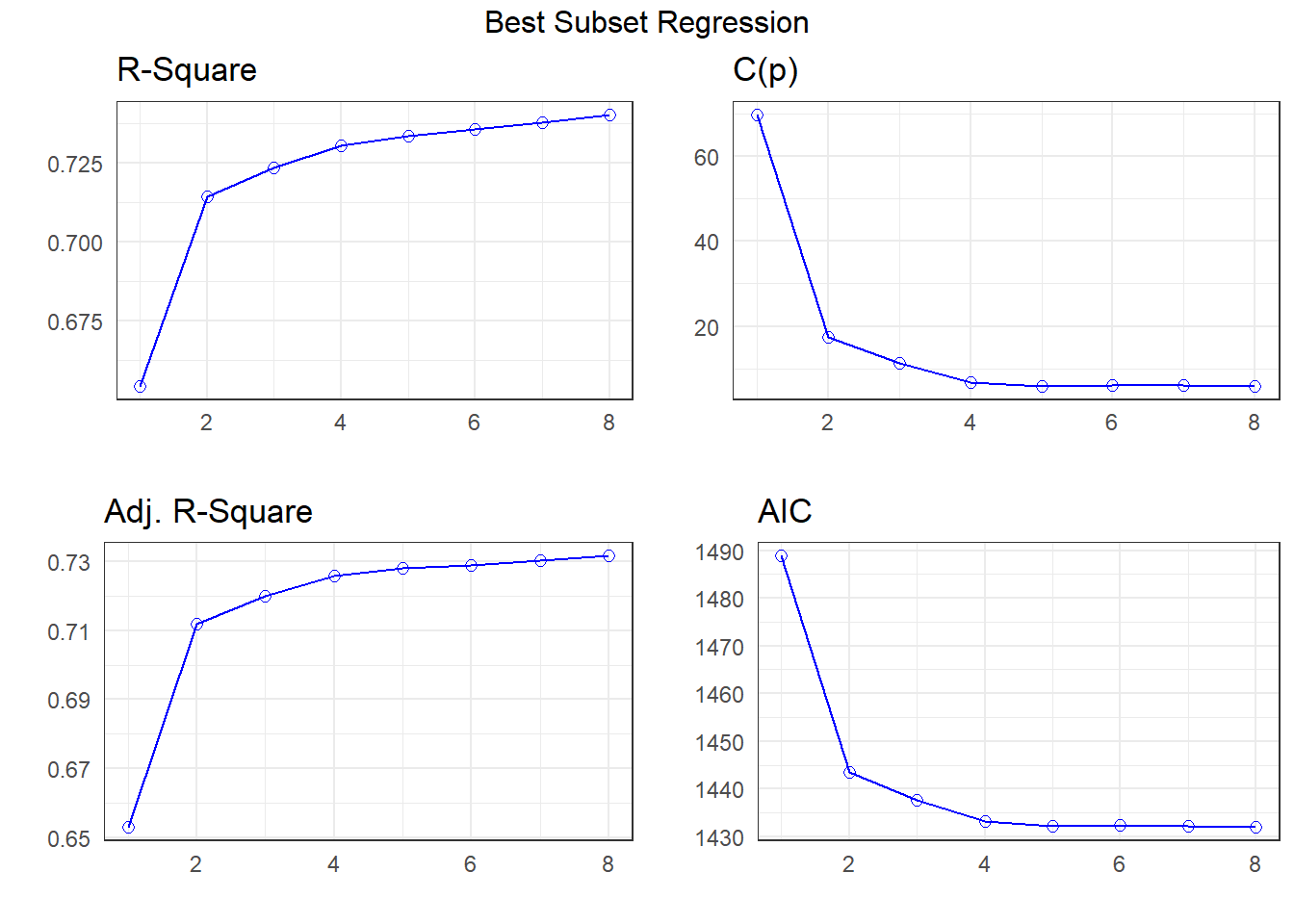
20.7 Four-Predictor Model
fit4 <- lm(
siri_bf ~ weight + abdomen + forearm + wrist,
data = bodyfat
) model_parameters(fit4, ci = 0.95)Parameter | Coefficient | SE | 95% CI | t(243) | p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
(Intercept) | -33.61 | 7.26 | [-47.91, -19.32] | -4.63 | < .001
weight | -0.14 | 0.02 | [ -0.19, -0.09] | -5.58 | < .001
abdomen | 0.99 | 0.06 | [ 0.88, 1.10] | 17.71 | < .001
forearm | 0.45 | 0.18 | [ 0.10, 0.81] | 2.51 | 0.013
wrist | -1.48 | 0.44 | [ -2.36, -0.61] | -3.34 | < .001
Uncertainty intervals (equal-tailed) and p-values (two-tailed) computed
using a Wald t-distribution approximation.model_performance(fit4)# Indices of model performance
AIC | AICc | BIC | R2 | R2 (adj.) | RMSE | Sigma
------------------------------------------------------------------
1433.207 | 1433.556 | 1454.288 | 0.730 | 0.726 | 4.248 | 4.291check_model(fit4)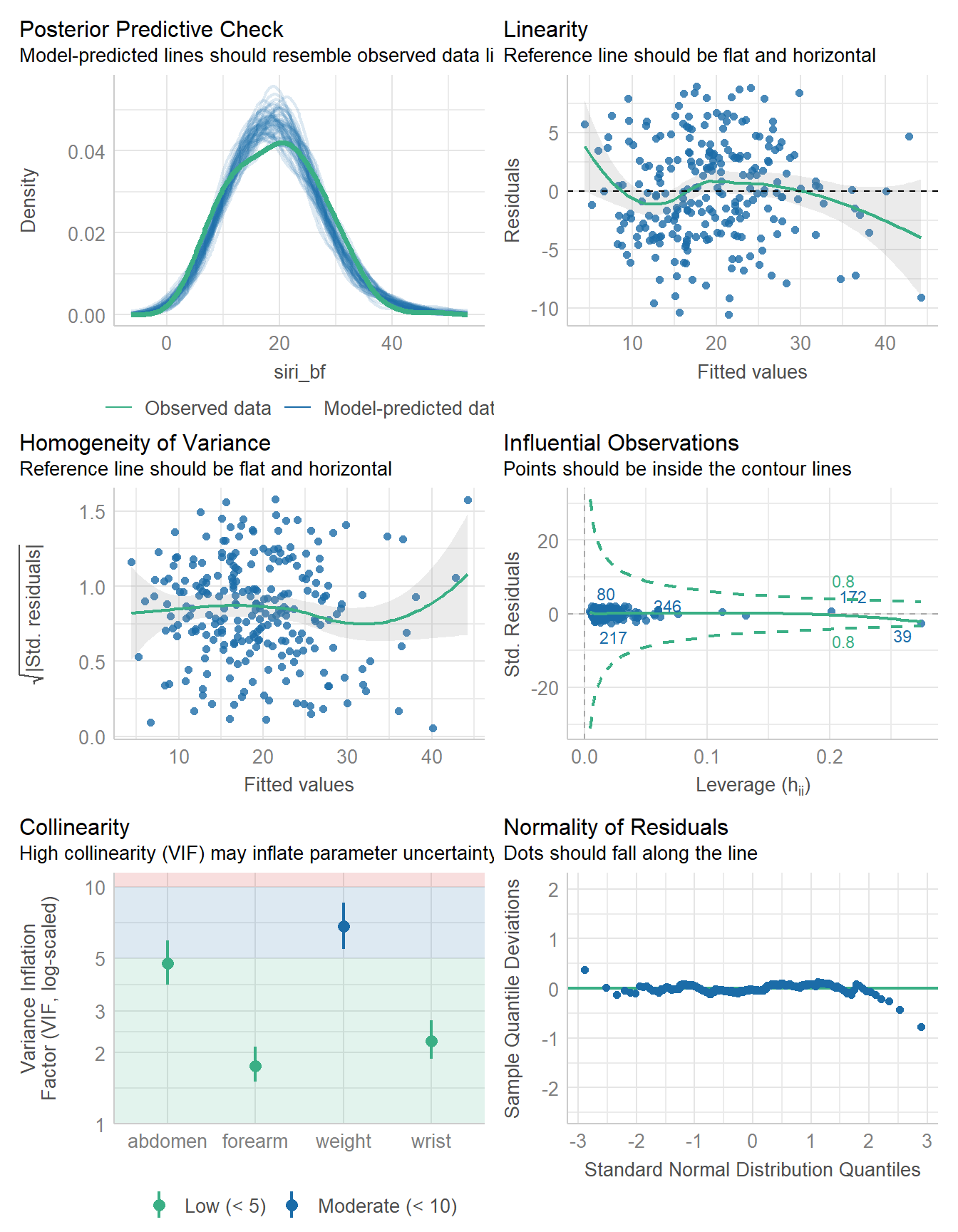
20.8 Five-Predictor Model
fit5 <- lm(
siri_bf ~ weight + neck + abdomen + forearm + wrist,
data = bodyfat
)model_parameters(fit5, ci = 0.95)Parameter | Coefficient | SE | 95% CI | t(242) | p
---------------------------------------------------------------------
(Intercept) | -29.23 | 7.67 | [-44.35, -14.11] | -3.81 | < .001
weight | -0.12 | 0.03 | [ -0.17, -0.07] | -4.81 | < .001
neck | -0.37 | 0.22 | [ -0.81, 0.06] | -1.70 | 0.090
abdomen | 1.00 | 0.06 | [ 0.89, 1.11] | 17.85 | < .001
forearm | 0.51 | 0.18 | [ 0.15, 0.87] | 2.79 | 0.006
wrist | -1.23 | 0.47 | [ -2.15, -0.31] | -2.62 | 0.009
Uncertainty intervals (equal-tailed) and p-values (two-tailed) computed
using a Wald t-distribution approximation.model_performance(fit5)# Indices of model performance
AIC | AICc | BIC | R2 | R2 (adj.) | RMSE | Sigma
------------------------------------------------------------------
1432.263 | 1432.730 | 1456.857 | 0.734 | 0.728 | 4.223 | 4.275check_model(fit5)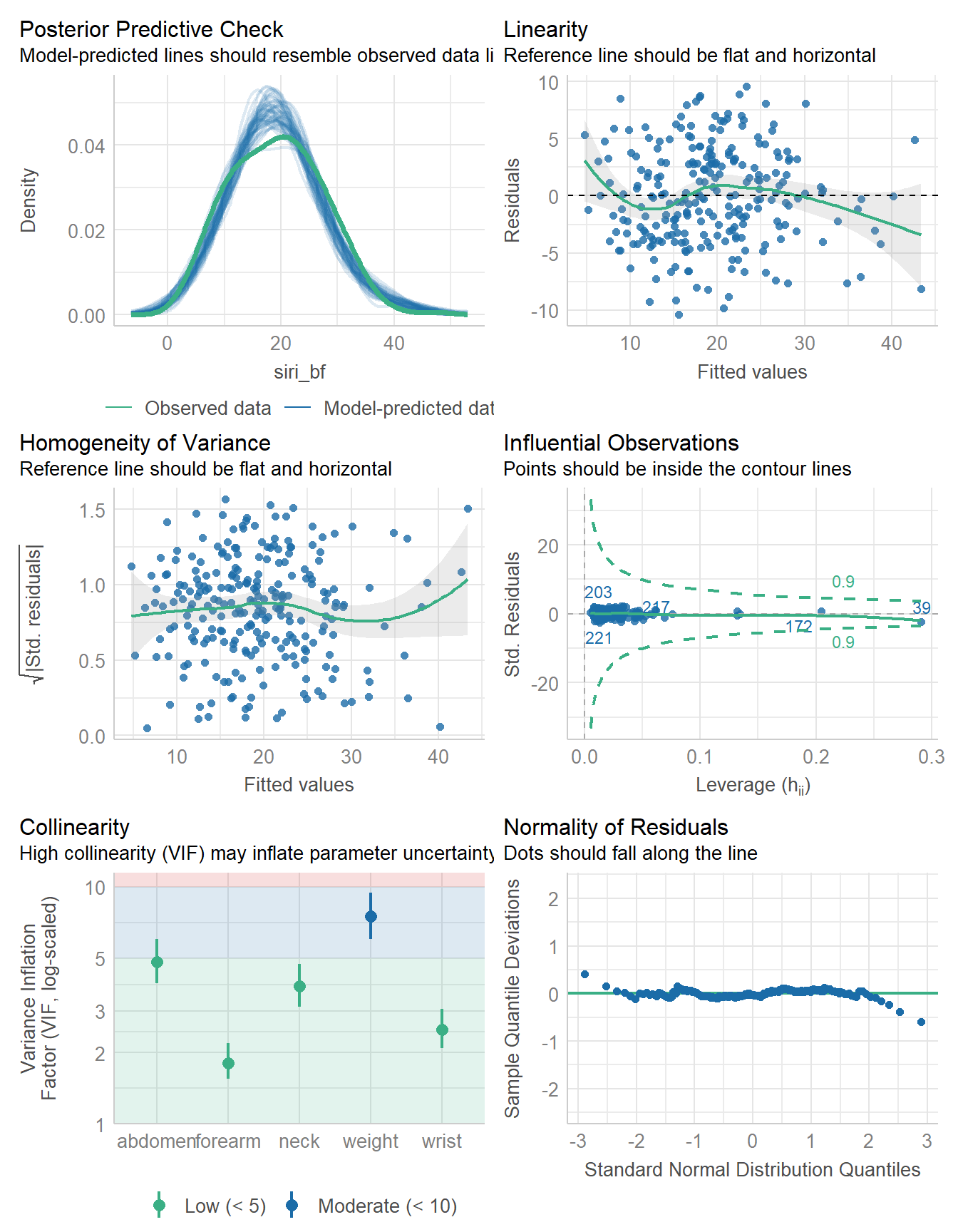
compare_performance(fit4, fit5)# Comparison of Model Performance Indices
Name | Model | AIC (weights) | AICc (weights) | BIC (weights) | R2 | R2 (adj.) | RMSE | Sigma
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
fit4 | lm | 1433.2 (0.384) | 1433.6 (0.398) | 1454.3 (0.783) | 0.730 | 0.726 | 4.248 | 4.291
fit5 | lm | 1432.3 (0.616) | 1432.7 (0.602) | 1456.9 (0.217) | 0.734 | 0.728 | 4.223 | 4.275set.seed(431)
performance_accuracy(fit1, method = "cv", k = 5)# Accuracy of Model Predictions
Accuracy (95% CI): 81.49% [73.12%, 92.09%]
Method: Correlation between observed and predictedset.seed(431)
performance_accuracy(fit2, method = "cv", k = 5)# Accuracy of Model Predictions
Accuracy (95% CI): 82.87% [74.24%, 93.11%]
Method: Correlation between observed and predictedset.seed(431)
performance_accuracy(fit4, method = "cv", k = 5)# Accuracy of Model Predictions
Accuracy (95% CI): 83.10% [74.74%, 92.71%]
Method: Correlation between observed and predictedset.seed(431)
performance_accuracy(fit5, method = "cv", k = 5)# Accuracy of Model Predictions
Accuracy (95% CI): 82.99% [74.96%, 93.04%]
Method: Correlation between observed and predictedset.seed(431)
performance_cv(fit1)# Cross-validation performance (30% holdout method)
MSE | RMSE | R2
-----------------
16 | 4 | 0.74set.seed(431)
performance_cv(fit2)# Cross-validation performance (30% holdout method)
MSE | RMSE | R2
-----------------
15 | 3.8 | 0.76set.seed(431)
performance_cv(fit4)# Cross-validation performance (30% holdout method)
MSE | RMSE | R2
-----------------
14 | 3.8 | 0.76set.seed(431)
performance_cv(fit5)# Cross-validation performance (30% holdout method)
MSE | RMSE | R2
-----------------
15 | 3.9 | 0.7520.9 Bayesian linear model
We’ll now refit the four-predictor model using stan_glm() and a weakly informative prior, as usual.
fit4b <- stan_glm(
siri_bf ~ weight + abdomen + forearm + wrist,
data = bodyfat, refresh = 0
) model_parameters(fit4b, ci = 0.95)Parameter | Median | 95% CI | pd | Rhat | ESS | Prior
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(Intercept) | -33.40 | [-48.11, -19.22] | 100% | 1.003 | 2889.00 | Normal (19.28 +- 20.49)
weight | -0.14 | [ -0.19, -0.09] | 100% | 1.004 | 2119.00 | Normal (0.00 +- 0.71)
abdomen | 0.99 | [ 0.87, 1.10] | 100% | 1.002 | 2402.00 | Normal (0.00 +- 1.92)
forearm | 0.45 | [ 0.09, 0.81] | 99.40% | 1.001 | 3820.00 | Normal (0.00 +- 10.20)
wrist | -1.49 | [ -2.35, -0.59] | 99.95% | 1.002 | 3160.00 | Normal (0.00 +- 22.30)
Uncertainty intervals (equal-tailed) and p-values (two-tailed) computed
using a MCMC distribution approximation.model_performance(fit4b)# Indices of model performance
ELPD | ELPD_SE | LOOIC | LOOIC_SE | WAIC | R2 | R2 (adj.) | RMSE | Sigma
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-717.386 | 9.726 | 1434.773 | 19.452 | 1434.619 | 0.727 | 0.716 | 4.248 | 4.300check_model(fit4b)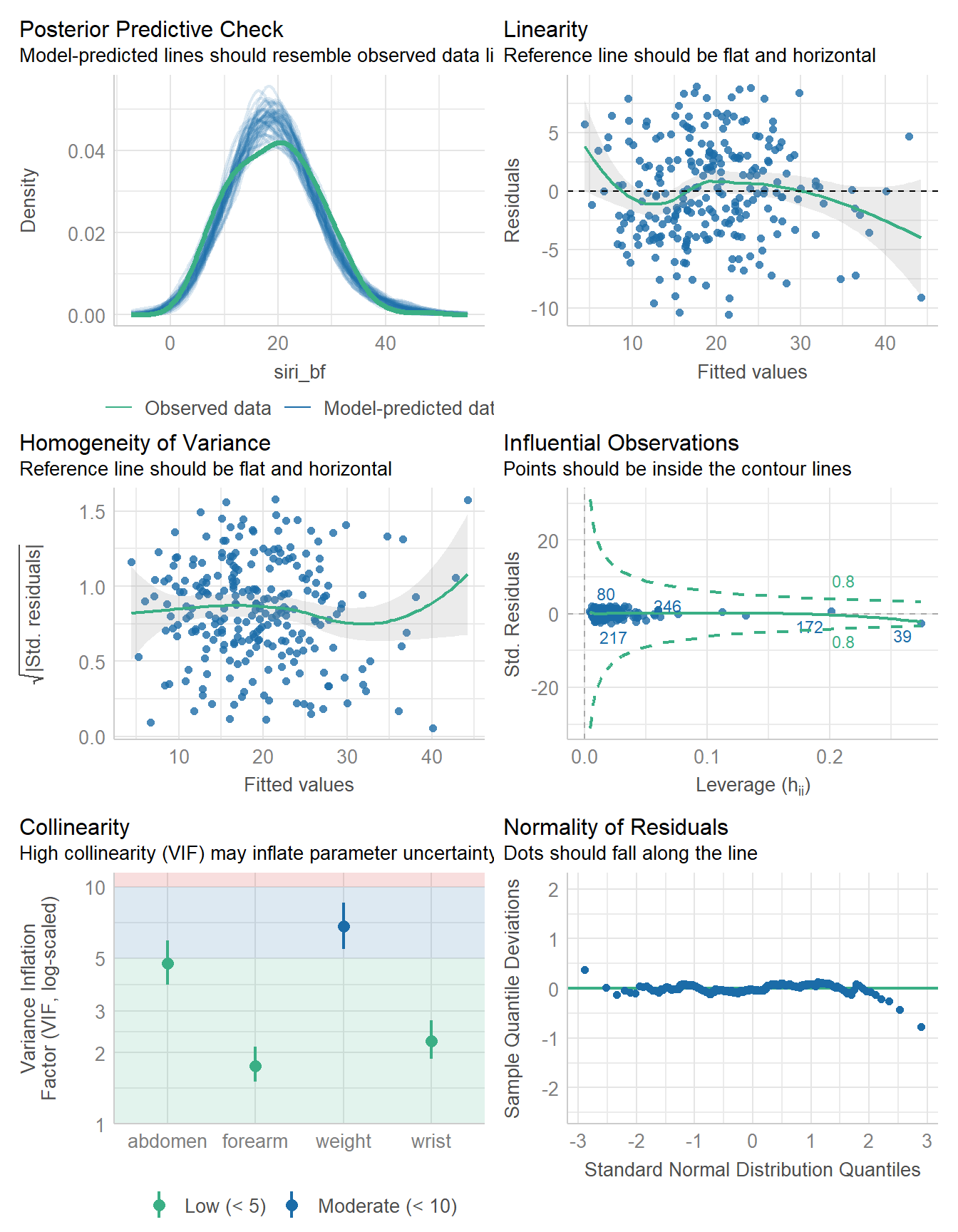
set.seed(431)
performance_accuracy(fit4b, method = "cv", k = 5)# Accuracy of Model Predictions
Accuracy (95% CI): 83.11% [74.77%, 92.71%]
Method: Correlation between observed and predictedset.seed(431)
performance_cv(fit4b)# Cross-validation performance (30% holdout method)
MSE | RMSE | R2
-----------------
14 | 3.8 | 0.76